Sudden Visual Loss
Etiology:
transient visual obscuration, TVO, papilledema, increased intracranial pressure, amaurosis fugax, monocular blindness, partial blindness, total blindness, transient monocular visual loss, TMVL, transient monocular blindness, TMB, transient bilateral visual loss, TBVL, ocular infarction, ischemic damage to the eye, internal carotid artery disease, ICA disease, angle-closure glaucoma, central retinal artery occlusion, CRAO, branch retinal artery occlusion, BRAO, ischemia of the optic nerve, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, AION, ruptured globe, sudden visual loss, decreased vision, nonarteric anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, NAION, migraine, scintillating scotoma, intraocular foreign body, cardiac disease, stenotic vascular disease, carotid or vertebral artery atherosclerotic disease, fibromuscular dysplasia, arteritis, carotid artery dissection, vertebral artery dissection, platelet-containing emboli, hypercoagulable states, antiphospholipid syndrome, anemia
Medicine, surgery,ophthalmology,psychiatry,dermatology,ENT disease,treatment,cure,diagnosis,complications, Medical cases Ebooks free downloads medical videos Gallery
Prader Willi Syndrome: A short Review
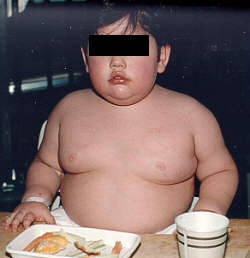
Prader-Willi syndrome (Summarized By Me)
simplified
Prader-Willi syndrome (abbreviated PWS) is a very rare genetic disorder, in which seven genes (or some subset thereof) on chromosome 15 are missing or unexpressed (chromosome 15q partial deletion) on the paternal chromosome.
Diagnosis/testing
genetic testing, specifically DNA-based methylation testing to detect the absence of the paternally contributed Prader-Willi syndrome/Angelman syndrome (PWS/AS) region on chromosome 15q11-q13. Such testing detects over 97% of patients. Methylation-specific testing is important to confirm the diagnosis of PWS in all individuals, but especially those who are too young to manifest sufficient features to make the diagnosis on clinical grounds or in those individuals who have atypical findings.
PWS phenotype
Clinical Features
Clinical Features
In Utero:
Reduced fetal movement
Frequent abnormal fetal position
At Birth:
Often breech or caesarean births
Lethargy
Hypotonia
Feeding difficulties (due to poor muscle tone affecting sucking reflex)
Difficulties establishing respiration
Hypogonadism
Infancy:
Failure to thrive (continued feeding difficulties)
Delayed milestones/intellectual delay
Excessive sleeping
Strabismus
Scoliosis (often not detected at birth)
Childhood:
Speech delay
Poor physical coordination
Hyperphagia (over-eating) from age 2 - 4 years. Note change from feeding difficulties in infancy
Excessive weight gain
Adolescence:
Delayed puberty
Short stature
Obesity
Extremely flexible
Adulthood:
Infertility (males and females)
Hypogonadism
Sparse pubic hair
Obesity
Hypotonia
Learning disabilities/borderline intellectual functioning (but some cases of average intelligence)
Proneness to diabetes mellitus
Extremely flexible
General physical appearance (adults)
Prominent nasal bridge
Small hands and feet
Soft skin, which is easily bruised
Excess fat, especially in the central portion of the body
High, narrow forehead
Almond shaped eyes with thin, down-turned lips
Light skin and hair relative to other family members
Lack of complete sexual development
Always picking at their skin
Stria
Delayed motor development
Reduced fetal movement
Frequent abnormal fetal position
At Birth:
Often breech or caesarean births
Lethargy
Hypotonia
Feeding difficulties (due to poor muscle tone affecting sucking reflex)
Difficulties establishing respiration
Hypogonadism
Infancy:
Failure to thrive (continued feeding difficulties)
Delayed milestones/intellectual delay
Excessive sleeping
Strabismus
Scoliosis (often not detected at birth)
Childhood:
Speech delay
Poor physical coordination
Hyperphagia (over-eating) from age 2 - 4 years. Note change from feeding difficulties in infancy
Excessive weight gain
Adolescence:
Delayed puberty
Short stature
Obesity
Extremely flexible
Adulthood:
Infertility (males and females)
Hypogonadism
Sparse pubic hair
Obesity
Hypotonia
Learning disabilities/borderline intellectual functioning (but some cases of average intelligence)
Proneness to diabetes mellitus
Extremely flexible
General physical appearance (adults)
Prominent nasal bridge
Small hands and feet
Soft skin, which is easily bruised
Excess fat, especially in the central portion of the body
High, narrow forehead
Almond shaped eyes with thin, down-turned lips
Light skin and hair relative to other family members
Lack of complete sexual development
Always picking at their skin
Stria
Delayed motor development
Neuro-cognitive
Individuals with PWS are at risk of learning and attention difficulties. Curfs and Frym (1992) conducted research into the varying degrees of learning disability found in Prader Willi Syndrome (PWS).[5] Their results were as follows:
5%...IQ above 85 (Average to low average intelligence)
27%..IQ 70 - 85 (Borderline intellectual functioning)
34%..IQ 50 - 70 (Mild intellectual disability)
27%..IQ 35 - 50 (Moderate intellectual disability)
5%...IQ 20 - 35 (Severe intellectual disability)
<1%..iq>
Individuals with PWS are at risk of learning and attention difficulties. Curfs and Frym (1992) conducted research into the varying degrees of learning disability found in Prader Willi Syndrome (PWS).[5] Their results were as follows:
5%...IQ above 85 (Average to low average intelligence)
27%..IQ 70 - 85 (Borderline intellectual functioning)
34%..IQ 50 - 70 (Mild intellectual disability)
27%..IQ 35 - 50 (Moderate intellectual disability)
5%...IQ 20 - 35 (Severe intellectual disability)
<1%..iq>
Behavioral
Prader-Willi syndrome is also frequently associated with an extreme and insatiable appetite, often resulting in morbid obesity. There is currently no consensus as to the cause for this particular symptom, although genetic abnormalities in chromosome 15 disrupt the normal functioning of the hypothalamus.[6] Given that the hypothalamus regulates many basic processes, including appetite, there may well be a link. However, no organic defect of the hypothalamus has been discovered on post mortem investigation.[6]
Prader-Willi syndrome is also frequently associated with an extreme and insatiable appetite, often resulting in morbid obesity. There is currently no consensus as to the cause for this particular symptom, although genetic abnormalities in chromosome 15 disrupt the normal functioning of the hypothalamus.[6] Given that the hypothalamus regulates many basic processes, including appetite, there may well be a link. However, no organic defect of the hypothalamus has been discovered on post mortem investigation.[6]
Endocrine
There are several aspects of PWS that support the concept of growth hormone deficiency in individuals with PWS. Specifically, individuals with PWS have short stature, are obese with abnormal body composition, have reduced fat free mass (FFM), have reduced LBM and total energy expenditure, and have decreased bone density.
PWS is characterized by hypogonadism. This is manifested as undescended testes in males and benign premature adrenarche in females. Testes may descend with time or can be managed with surgery or testosterone replacement. Adrenarche may be treated with hormone replacement therapy.
Treatment
Prader-Willi syndrome has no cure. However, several treatments are in place to lessen the condition's symptoms. Growth hormone replacement therapy improves body composition and increases linear height. During infancy, subjects should undergo therapies to improve muscle tone. Speech and occupational therapy are also indicated. During the school years, children benefit from a highly structured learning environment as well as extra help. Throughout their lives, the subject's food should literally be kept under lock and key, since the largest problem associated with the syndrome is severe obesity.
Because of severe obesity, obstructive sleep apnea is a common sequela, and a CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) machine is often needed.
List Of All Infectious Diseases
Viral infectious diseases
AIDS – Chickenpox (Varicella) – Common cold – Cytomegalovirus Infection – Colorado tick fever – Dengue fever – Ebola hemorrhagic fever – Hand, foot and mouth disease – Hepatitis – Herpes simplex – Herpes zoster – HPV – Influenza (Flu) – Lassa fever – Measles – Marburg hemorrhagic fever – Infectious mononucleosis – Mumps – Norovirus – Poliomyelitis – Progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy – Rabies – Rubella – SARS – Smallpox (Variola) – Viral encephalitis – Viral gastroenteritis – Viral meningitis – Viral pneumonia – West Nile disease – Yellow feverBacterial Anthrax –
Bacterial
Meningitis –
Botulism – Brucellosis – Campylobacteriosis – Cat Scratch Disease – Cholera – Diphtheria – Epidemic Typhus – Gonorrhea – Impetigo– Legionellosis – Leprosy (Hansen's Disease) – Leptospirosis – Listeriosis – Lyme disease – Melioidosis – Rheumatic Fever;MRSA infection – Nocardiosis – Pertussis (Whooping Cough) – Plague – Pneumococcal pneumonia – Psittacosis – Q fever – Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) – Salmonellosis – Scarlet Fever – Shigellosis – Syphilis – Tetanus – Trachoma – Tuberculosis – Tularemia – Typhoid Fever – Typhus– Urinary Tract Infections
Parasitic infectious diseases
African trypanosomiasis – Amebiasis – Ascariasis – Babesiosis – Chagas Disease – Clonorchiasis – Cryptosporidiosis – Cysticercosis – Diphyllobothriasis – Dracunculiasis – Echinococcosis – Enterobiasis – Fascioliasis – Fasciolopsiasis – Filariasis – Free-living amebic infection – Giardiasis – Gnathostomiasis – Hymenolepiasis – Isosporiasis – Kala-azar – Leishmaniasis – Malaria – Metagonimiasis – Myiasis – Onchocerciasis – Pediculosis – Pinworm Infection – Scabies – Schistosomiasis – Taeniasis – Toxocariasis – Toxoplasmosis – Trichinellosis – Trichinosis – Trichuriasis – Trichomoniasis – Trypanosomiasis
Fungal infectious diseases
Aspergillosis – Blastomycosis – Candidiasis – Coccidioidomycosis – Cryptococcosis – Histoplasmosis – Tinea pedisPrion infectious diseases transmissible spongiform encephalopathy – Bovine spongiform encephalopathy – Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease – Kuru–Fatal Familial Insomnia–Alpers Syndrome –
AIDS – Chickenpox (Varicella) – Common cold – Cytomegalovirus Infection – Colorado tick fever – Dengue fever – Ebola hemorrhagic fever – Hand, foot and mouth disease – Hepatitis – Herpes simplex – Herpes zoster – HPV – Influenza (Flu) – Lassa fever – Measles – Marburg hemorrhagic fever – Infectious mononucleosis – Mumps – Norovirus – Poliomyelitis – Progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy – Rabies – Rubella – SARS – Smallpox (Variola) – Viral encephalitis – Viral gastroenteritis – Viral meningitis – Viral pneumonia – West Nile disease – Yellow feverBacterial Anthrax –
Bacterial
Meningitis –
Botulism – Brucellosis – Campylobacteriosis – Cat Scratch Disease – Cholera – Diphtheria – Epidemic Typhus – Gonorrhea – Impetigo– Legionellosis – Leprosy (Hansen's Disease) – Leptospirosis – Listeriosis – Lyme disease – Melioidosis – Rheumatic Fever;MRSA infection – Nocardiosis – Pertussis (Whooping Cough) – Plague – Pneumococcal pneumonia – Psittacosis – Q fever – Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) – Salmonellosis – Scarlet Fever – Shigellosis – Syphilis – Tetanus – Trachoma – Tuberculosis – Tularemia – Typhoid Fever – Typhus– Urinary Tract Infections
Parasitic infectious diseases
African trypanosomiasis – Amebiasis – Ascariasis – Babesiosis – Chagas Disease – Clonorchiasis – Cryptosporidiosis – Cysticercosis – Diphyllobothriasis – Dracunculiasis – Echinococcosis – Enterobiasis – Fascioliasis – Fasciolopsiasis – Filariasis – Free-living amebic infection – Giardiasis – Gnathostomiasis – Hymenolepiasis – Isosporiasis – Kala-azar – Leishmaniasis – Malaria – Metagonimiasis – Myiasis – Onchocerciasis – Pediculosis – Pinworm Infection – Scabies – Schistosomiasis – Taeniasis – Toxocariasis – Toxoplasmosis – Trichinellosis – Trichinosis – Trichuriasis – Trichomoniasis – Trypanosomiasis
Fungal infectious diseases
Aspergillosis – Blastomycosis – Candidiasis – Coccidioidomycosis – Cryptococcosis – Histoplasmosis – Tinea pedisPrion infectious diseases transmissible spongiform encephalopathy – Bovine spongiform encephalopathy – Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease – Kuru–Fatal Familial Insomnia–Alpers Syndrome –
Marfan Syndome: Tall is not always Gold
Marfan syndrome
is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder of the connective tissue characterized by disproportionately long limbs, long thin fingers, a typically tall stature, and a predisposition to cardiovascular abnormalities, specifically those affecting the heart valves and aorta. The disorder may also affect numerous other structures and organs — including the lungs, eyes, dural sac surrounding the spinal cord, and hard palate. It is named after Antoine Marfan, the French pediatrician
Symptoms
Three systems are predominantly affected.
Ocular:
upward lens dislocation
retinal detachment
Skeletal:
arachnodactyly
tall with disproportionately long legs and arms - the span of the arms is greater than the height
pectus excavatum
spinal abnormalities - spondylolisthesis, scoliosis
increased incidence of slipped upper femoral epiphysis
generalised joint laxity with predisposition to flat feet or dislocation of patella or shoulder
Cardiovascular
- affecting the aortic and mitral valves and the ascending aorta:
dilatation of the aorta may be noted at any age, beginning at the aortic valve and usually confined to the ascending aorta
aortic insufficiency may result from stretching of the aortic valve ring and a dissecting aneurysm of the aorta may be a terminal event. Rarely, it occurs during pregnancy
mitral insufficiency results from redundant cusps and chordae tendineae
other cardiac malformations have occasionally been reported
Mental development is normal.
The average lifespan of an affected individual is 40 to 50 years.
Skeletal system
The most readily visible signs are associated with the skeletal system. Many individuals with Marfan Syndrome grow to above average height. Some have long slender limbs with fingers and toes that are also abnormally long and slender (arachnodactyly). This long, slender body habitus and long, slender limbs are known as dolichostenomelia. An individual's arms may be disproportionately long, with thin, weak wrists. In addition to affecting height and limb proportions, Marfan syndrome can produce other skeletal signs. Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis) is common, as is abnormal indentation (pectus excavatum) or protrusion (pectus carinatum) of the sternum. Other signs include abnormal joint flexibility, a high palate, malocclusions, flat feet, stooped shoulders, unexplained stretch marks on the skin and thin wrists. Some people with Marfan have speech disorders resulting from symptomatic high palates and small jaws.
Eyes
Marfan syndrome can also seriously affect the eyes and vision. Nearsightedness and astigmatism are common, but farsightedness can also result. Periodic eye exams can lead to an ophthalmologist or optometrist discovering dislocation, or subluxation, of the crystalline lens in one or both eyes (ectopia lentis) by carefully observing these structures using a slit-lamp biomicroscope. This can be differentiated from the similar condition homocystinuria, where the dislocation is inferonasal; in Marfan's the dislocation is superotemporal. Sometimes eye problems appear only after the weakening of connective tissue has caused detachment of the retina.Early onset glaucoma can be another complication.
Cardiovascular system
The most serious conditions associated with Marfan syndrome involve the cardiovascular system. Undue fatigue, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, racing heartbeats, or pain in the left chest, back, shoulder, or arm, can bring a person into the doctor's office. Cold arms, hands and feet can also be seriously linked to marfan syndrome because of a loss of blood circulation. A heart murmur heard on a stethoscope, an abnormal reading on an electrocardiogram, or symptoms of angina can lead a doctor to order an echocardiogram. This can reveal signs of leakage or prolapse of the mitral or aortic valves that control the flow of blood through the heart. (See mitral valve prolapse.) However, the major sign that would lead a doctor to consider an underlying condition is a dilated aorta or an aortic aneurysm. Sometimes, no heart problems are apparent until the weakening of the connective tissue in the ascending aorta causes an aortic aneurysm or even aortic dissection.
Lungs
Marfan syndrome is a risk factor for spontaneous pneumothorax. In spontaneous unilateral pneumothorax, air escapes from a lung and occupies the pleural space between the chest wall and a lung. The lung becomes partially compressed or collapsed. This can cause pain, shortness of breath, cyanosis, and, if not treated, death. Marfan syndrome has also been associated with sleep apnea and idiopathic obstructive lung disease.
Central nervous system
Another condition that can reduce the quality of life for an individual, though not life-threatening, is dural ectasia, the weakening of the connective tissue of the dural sac, the membrane that encases the spinal cord. Dural ectasia can be present for a long time without producing any noticeable symptoms. Symptoms that can occur are lower back pain, leg pain, abdominal pain, other neurological symptoms in the lower extremities, or headaches. Such symptoms usually diminish when the individual lies flat on his or her back. These types of symptoms might lead a doctor to order an X-ray of the lower spine. Dural ectasia is usually not visible on an X-ray in the early phases. A worsening of symptoms and the lack of finding any other cause should eventually lead a doctor to order an upright MRI of the lower spine. Dural ectasia that has progressed to the point of causing these symptoms would appear in an upright MRI image as a dilated pouch that is wearing away at the lumbar vertebrae. Other spinal issues associated with Marfan include degenerative disk disease and spinal cysts.
is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder of the connective tissue characterized by disproportionately long limbs, long thin fingers, a typically tall stature, and a predisposition to cardiovascular abnormalities, specifically those affecting the heart valves and aorta. The disorder may also affect numerous other structures and organs — including the lungs, eyes, dural sac surrounding the spinal cord, and hard palate. It is named after Antoine Marfan, the French pediatrician
Symptoms
Three systems are predominantly affected.
Ocular:
upward lens dislocation
retinal detachment
Skeletal:
arachnodactyly
tall with disproportionately long legs and arms - the span of the arms is greater than the height
pectus excavatum
spinal abnormalities - spondylolisthesis, scoliosis
increased incidence of slipped upper femoral epiphysis
generalised joint laxity with predisposition to flat feet or dislocation of patella or shoulder
Cardiovascular
- affecting the aortic and mitral valves and the ascending aorta:
dilatation of the aorta may be noted at any age, beginning at the aortic valve and usually confined to the ascending aorta
aortic insufficiency may result from stretching of the aortic valve ring and a dissecting aneurysm of the aorta may be a terminal event. Rarely, it occurs during pregnancy
mitral insufficiency results from redundant cusps and chordae tendineae
other cardiac malformations have occasionally been reported
Mental development is normal.
The average lifespan of an affected individual is 40 to 50 years.
Skeletal system
The most readily visible signs are associated with the skeletal system. Many individuals with Marfan Syndrome grow to above average height. Some have long slender limbs with fingers and toes that are also abnormally long and slender (arachnodactyly). This long, slender body habitus and long, slender limbs are known as dolichostenomelia. An individual's arms may be disproportionately long, with thin, weak wrists. In addition to affecting height and limb proportions, Marfan syndrome can produce other skeletal signs. Abnormal curvature of the spine (scoliosis) is common, as is abnormal indentation (pectus excavatum) or protrusion (pectus carinatum) of the sternum. Other signs include abnormal joint flexibility, a high palate, malocclusions, flat feet, stooped shoulders, unexplained stretch marks on the skin and thin wrists. Some people with Marfan have speech disorders resulting from symptomatic high palates and small jaws.
Eyes
Marfan syndrome can also seriously affect the eyes and vision. Nearsightedness and astigmatism are common, but farsightedness can also result. Periodic eye exams can lead to an ophthalmologist or optometrist discovering dislocation, or subluxation, of the crystalline lens in one or both eyes (ectopia lentis) by carefully observing these structures using a slit-lamp biomicroscope. This can be differentiated from the similar condition homocystinuria, where the dislocation is inferonasal; in Marfan's the dislocation is superotemporal. Sometimes eye problems appear only after the weakening of connective tissue has caused detachment of the retina.Early onset glaucoma can be another complication.
Cardiovascular system
The most serious conditions associated with Marfan syndrome involve the cardiovascular system. Undue fatigue, shortness of breath, heart palpitations, racing heartbeats, or pain in the left chest, back, shoulder, or arm, can bring a person into the doctor's office. Cold arms, hands and feet can also be seriously linked to marfan syndrome because of a loss of blood circulation. A heart murmur heard on a stethoscope, an abnormal reading on an electrocardiogram, or symptoms of angina can lead a doctor to order an echocardiogram. This can reveal signs of leakage or prolapse of the mitral or aortic valves that control the flow of blood through the heart. (See mitral valve prolapse.) However, the major sign that would lead a doctor to consider an underlying condition is a dilated aorta or an aortic aneurysm. Sometimes, no heart problems are apparent until the weakening of the connective tissue in the ascending aorta causes an aortic aneurysm or even aortic dissection.
Lungs
Marfan syndrome is a risk factor for spontaneous pneumothorax. In spontaneous unilateral pneumothorax, air escapes from a lung and occupies the pleural space between the chest wall and a lung. The lung becomes partially compressed or collapsed. This can cause pain, shortness of breath, cyanosis, and, if not treated, death. Marfan syndrome has also been associated with sleep apnea and idiopathic obstructive lung disease.
Central nervous system
Another condition that can reduce the quality of life for an individual, though not life-threatening, is dural ectasia, the weakening of the connective tissue of the dural sac, the membrane that encases the spinal cord. Dural ectasia can be present for a long time without producing any noticeable symptoms. Symptoms that can occur are lower back pain, leg pain, abdominal pain, other neurological symptoms in the lower extremities, or headaches. Such symptoms usually diminish when the individual lies flat on his or her back. These types of symptoms might lead a doctor to order an X-ray of the lower spine. Dural ectasia is usually not visible on an X-ray in the early phases. A worsening of symptoms and the lack of finding any other cause should eventually lead a doctor to order an upright MRI of the lower spine. Dural ectasia that has progressed to the point of causing these symptoms would appear in an upright MRI image as a dilated pouch that is wearing away at the lumbar vertebrae. Other spinal issues associated with Marfan include degenerative disk disease and spinal cysts.
Sinusitis : A common cause of Headache
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, which may or may not be as a result of infection, from bacterial, fungal, viral, allergic or autoimmune issues. Newer classifications of sinusitis refer to it as rhinosinusitis, taking into account the thought that inflammation of the sinuses cannot occur without some inflammation of the nose as well (rhinitis).
Types Of Sinusitis: ( BY LOCATION)
Maxillary sinusitis - can cause pain or pressure in the maxillary (cheek) area (e.g., toothache, headache) Frontal sinusitis - can cause pain or pressure in the frontal sinus cavity (located behind/above eyes), headache
Ethmoid sinusitis - can cause pain or pressure pain between/behind eyes, headache
Sphenoid sinusitis - can cause pain or pressure behind the eyes, but often refers to the vertex of the head
Acute sinusitis
Acute sinusitis is usually precipitated by an earlier upper respiratory tract infection, generally of viral origin. Virally damaged surface tissues are then colonized by bacteria, most commonly Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Moraxella catarrhalis and Staphylococcus aureus.
Other bacterial pathogens include other streptococci species, anaerobic bacteria and, less commonly, gram negative bacteria. Another possible cause of sinusitis can be dental problems that affect the maxillary sinus. Acute episodes of sinusitis can also result from fungal invasion. These infections are most often seen in patients with diabetes or other immune deficiencies (such as AIDS or transplant patients on anti-rejection medications) and can be life threatening. In type I diabetes, ketoacidosis causes sinusitis by Mucormycosis.
Chronic sinusitisChronic sinusitis is a complicated spectrum of diseases that share chronic inflammation of the sinuses in common. The causes are multifactorial and may include allergy, environmental factors such as dust or pollution, bacterial infection, or fungus (either allergic, infective, or reactive). Non allergic factors such as Vasomotor rhinitis can also cause chronic sinus problems. Abnormally narrow sinus passages, which can impede drainage from the sinus cavities, can also be a factor.
Symptoms include: Nasal congestion; facial pain; headache; fever; general malaise; thick green or yellow discharge; blurred vision, feeling of facial 'fullness' worsening on bending over; aching teeth.Very rarely, chronic sinusitis can lead to Anosmia, the inability to smell or detect odors.
A more recent, and still debated, development in chronic sinusitis is the role that fungus may play.
Predisposing Factors: deviated septum or small sinus ostia; smoking; nasal polyps; carrying the cystic fibrosis gene prior bouts of sinusitis
Other bacterial pathogens include other streptococci species, anaerobic bacteria and, less commonly, gram negative bacteria. Another possible cause of sinusitis can be dental problems that affect the maxillary sinus. Acute episodes of sinusitis can also result from fungal invasion. These infections are most often seen in patients with diabetes or other immune deficiencies (such as AIDS or transplant patients on anti-rejection medications) and can be life threatening. In type I diabetes, ketoacidosis causes sinusitis by Mucormycosis.
Chronic sinusitisChronic sinusitis is a complicated spectrum of diseases that share chronic inflammation of the sinuses in common. The causes are multifactorial and may include allergy, environmental factors such as dust or pollution, bacterial infection, or fungus (either allergic, infective, or reactive). Non allergic factors such as Vasomotor rhinitis can also cause chronic sinus problems. Abnormally narrow sinus passages, which can impede drainage from the sinus cavities, can also be a factor.
Symptoms include: Nasal congestion; facial pain; headache; fever; general malaise; thick green or yellow discharge; blurred vision, feeling of facial 'fullness' worsening on bending over; aching teeth.Very rarely, chronic sinusitis can lead to Anosmia, the inability to smell or detect odors.
A more recent, and still debated, development in chronic sinusitis is the role that fungus may play.
Predisposing Factors: deviated septum or small sinus ostia; smoking; nasal polyps; carrying the cystic fibrosis gene prior bouts of sinusitis
Treatment
Acute sinusitis
nasal irrigation or jala neti using a warm saline solution, hot drinks including tea and chicken soup, over-the-counter decongestants and nasal sprays, and getting plenty of rest. Analgesics (such as aspirin, paracetamol (acetaminophen) or ibuprofen) can be used, but caution must be employed to make sure the patient does not suffer from aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) as this could lead to anaphylaxis.
(Amoxicillin usually being the most common) with amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin/Co-Amoxiclav) being indicated for patients who fail amoxicillin alone. Fluoroquinolones may be used in patients who are allergic to penicillinsDoxycycline is also used by some, for patients who are penicillin allergic
Acute sinusitis
nasal irrigation or jala neti using a warm saline solution, hot drinks including tea and chicken soup, over-the-counter decongestants and nasal sprays, and getting plenty of rest. Analgesics (such as aspirin, paracetamol (acetaminophen) or ibuprofen) can be used, but caution must be employed to make sure the patient does not suffer from aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD) as this could lead to anaphylaxis.
(Amoxicillin usually being the most common) with amoxicillin/clavulanate (Augmentin/Co-Amoxiclav) being indicated for patients who fail amoxicillin alone. Fluoroquinolones may be used in patients who are allergic to penicillinsDoxycycline is also used by some, for patients who are penicillin allergic
Chronic sinusitis
Simple measuresNasal irrigation and flush promotes sinus cavity z health, andpatients with chronic sinusitis including symptoms of facial pain, headache, halitosis, cough, anterior rhinorrhea (watery discharge) and nasal congestion found nasal irrigation to be "just as effective at treating these symptoms as the drug therapies." In other studies, "daily hypertonic saline nasal irrigation improves sinus-related quality of life, decreases symptoms, and decreases medication use in patients with frequent sinusitis," and is "recommended as an effective adjunctive treatment of chronic sinonasal symptoms.
Medical approaches
FESS - functional endoscopic sinus surgery, whereby normal clearance from the sinuses is restored by removing the anatomical and pathological obstructive variations that predispose to sinusitis. This replaces prior open techniques requiring facial or oral incisions and refocuses the technique to the natural openings of the sinuses instead of promoting drainage by gravity, the idea upon which the Caldwell-Luc surgery was based
balloon sinuplasty
Endoscopic nasal Surgery allows more functional approach than by radical antrostomy. Intranasal endoscopic operations permits minimal trauma to adjacent tissues and precise removal of the diseased mucosa. intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy middle meatal antrostomy Caldwell-Luc radical antrostomy
ComplicationsIntracranial Complications -"meningitis""abscess",
Orbital Complications Orbital CellulitisOrbital Abscess
Vascular Complications -Infections aneurysms or infected blood clots in the intracranial cavity, both of which are potentially fatal.
Asthma Loss of Smell and Taste - ngs. Osteomyelitis
Simple measuresNasal irrigation and flush promotes sinus cavity z health, andpatients with chronic sinusitis including symptoms of facial pain, headache, halitosis, cough, anterior rhinorrhea (watery discharge) and nasal congestion found nasal irrigation to be "just as effective at treating these symptoms as the drug therapies." In other studies, "daily hypertonic saline nasal irrigation improves sinus-related quality of life, decreases symptoms, and decreases medication use in patients with frequent sinusitis," and is "recommended as an effective adjunctive treatment of chronic sinonasal symptoms.
Medical approaches
FESS - functional endoscopic sinus surgery, whereby normal clearance from the sinuses is restored by removing the anatomical and pathological obstructive variations that predispose to sinusitis. This replaces prior open techniques requiring facial or oral incisions and refocuses the technique to the natural openings of the sinuses instead of promoting drainage by gravity, the idea upon which the Caldwell-Luc surgery was based
balloon sinuplasty
Endoscopic nasal Surgery allows more functional approach than by radical antrostomy. Intranasal endoscopic operations permits minimal trauma to adjacent tissues and precise removal of the diseased mucosa. intranasal inferior meatal antrostomy middle meatal antrostomy Caldwell-Luc radical antrostomy
ComplicationsIntracranial Complications -"meningitis""abscess",
Orbital Complications Orbital CellulitisOrbital Abscess
Vascular Complications -Infections aneurysms or infected blood clots in the intracranial cavity, both of which are potentially fatal.
Asthma Loss of Smell and Taste - ngs. Osteomyelitis
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)